Products sold in Japan, such as laptops, APs, routers, landlines, mobile phones, LTE to Wi-Fi conversion, Bluetooth headsets, etc., need to be Giteki certified as long as they are sold in Japan. And the Giteki logo and the number issued must be affixed or printed on the certified products. If this certification is not done, it is illegal to sell directly in Japan and will be severely punished. Giteki certification is a mandatory certification.
Giteki certification logo, see the picture above
Japan's giteki certification as a whole relies on the certification based on the Radio Waves Law and the Telecommunications Business Law promulgated by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). The logo in the above picture is the giteki logo, which comes from the romanization
of the Japanese kanji (技適) for the Japanese name for the certification logo (技適マーク). Because it has been mentioned in the previous paragraph that giteki certification actually includes two types of certification: one is the "technical benchmark suitability certificate" that relies on the Japanese Radio Law; the other is the "technical benchmark suitability certification" that relies on the Japanese Electrical Communications Business Law. Because both types of certifications have the Chinese character "技適". So they are collectively called: giteki certification. Compared with the name of MIC certification, it is actually more accurate to call it giteki certification based on the final certification mark. About
the accuracy of the names of giteki, MIC, Telec, and Jate certifications In mainland
China , there are often certification laboratories or agencies that randomly call this type of certification in Japan Telec certification or Jate certification, etc. In fact, this name is inaccurate.
The full name of Telec is: Telecom Engineering Center. It was the first legal institution in Japan to conduct radio wave certification in the early days, so some people in mainland China mistakenly believed that Japan's giteki certification was telec certification. In fact, in the early days, TELEC could only certify the radio waves of giteki, but not the telecommunications business. Of course, in July 2014, TELEC finally obtained the certification qualification for Japan's telecommunications business.
The full name of Jate is: Japan Approvals Institute for Telecommunications Equipment, which was registered in April 1985. In the early days, it was the first legal institution in Japan to conduct certification under the Telecommunications Business Act, so some people in mainland China mistakenly believe that Japan's giteki certification is Jate certification. In fact, up to now, JATE only does certification for telecommunications business and does not accept certification for radio waves. In
summary, both JATE and TELEC are only certification agencies recognized by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications of Japan. It is obviously inappropriate and wrong to call Japan's technical benchmark suitability certification and technical benchmark suitability recognition JATE or TELEC certification. Just like China's CCC certification, CQC (China Quality Certification Center) can issue CCC certification in certain aspects, but we still call it CCC certification according to the official name, and few people call it CQC certification. Because CQC is just a certification body authorized by CCC certification.
Then calling it MIC certification is obviously based on the English abbreviation (MIC) of the Japanese Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, which is more standard than JATE and TELEC. But MIC is also just the certification and supervision department of Japan's radio and telecommunications industry. So again, analogous to China's CCC, the standard regulations for CCC certification are the rules issued by the CNCA China National Certification and Accreditation Administration. But we did not call this certification CNCA certification, but still called it CCC certification according to the certification mark. Therefore, by analogy, the certification for Japanese radio and telecommunications products is uniformly called giteki certification, which is actually the most standard name. Japan calls the mark on the product after this kind of certification "technical suitability mark".
About the Technical Benchmark Suitability Certification
The Technical Benchmark Suitability Certification is actually what is commonly known as the Japanese Radio Law Certification in mainland China. This certification includes three categories: Technical Benchmark Suitability Certification, Engineering Design Certification, and Technical Benchmark Suitability Self-confirmation.
Technical benchmark suitability certification: means that every device sold in Japan must undergo laboratory testing to indicate that the product complies with the requirements of the Radio Law. After passing the certification, each device submitted for inspection will have the giteki logo affixed to the product label, and each device will have a unique radio certification number.
Construction design certification: equivalent to the commonly said type certification. In other words, if you produce a model of product, you only need to take a few devices to the laboratory for testing. After passing the certification, each device of this model can have the giteki logo and the same radio certification number affixed to the product label.
Technical benchmark suitability self-confirmation: only suitable for the classification of " specially specified wireless devices " in the certification classification, corresponding to Article 38, 33, Paragraph 1 of the Japanese Radio Law .
About technical benchmark suitability certification
Technical benchmark suitability certification is actually what is commonly known as the Japanese Telecommunications Business Law Certification in mainland China. This certification includes three categories: technical benchmark suitability certification, design certification, and technical benchmark suitability self-confirmation.
Technical benchmark suitability certification: means that every device sold in Japan must undergo laboratory testing to indicate that the product complies with the requirements of the Electric Communications Business Law. After the certification is passed, each device sent for inspection will have the Giteki logo affixed to the product label, and each device will have a unique certification number for different electrical and telecommunications businesses.
Design certification: Equivalent to what is commonly called type certification. In other words, if you produce a certain model of product, you only need to take a few devices to the laboratory for testing. After the certification is passed, each device of this model can have the Giteki logo and the same telecommunications certification number affixed to the product label. Technical benchmarks are suitable for self-confirmation: Only suitable for the category classified as " specific terminal equipment "
in the certification classification .
Test content
Take the Wireless Access Point (AP) as an example. This type of product needs to be certified by the Japanese Radio Law because it transmits Wi-Fi signals in the 2.4G and 5G frequency bands. At the same time, if there is a 5G frequency band, DFS and TPC tests are also required according to Japanese regulations. This is to meet the Japanese Radio Law's requirement of not interfering with 5G radar frequencies.
So, for AP products like this, is it enough to just do the Radio Law? The Telecommunications Business Law mainly targets telecommunications equipment such as telephones and mobile phones. Is it not necessary to do it? The answer is definitely yes. Because this type of WLAN wireless access product will be directly or indirectly connected to the telecommunications network, it also needs to be certified by the Telecommunications Business Law.
The companies that have passed the Japanese giteki certification for this type of product in mainland China mainly include wireless AP products of Huawei, Sitka Spruce and other companies, and similar Aruba, Cisco, Ruckus and other companies have also passed the giteki certification for many products. Japan's giteki certification requirements are relatively strict, and the certification audit test data requirements are also relatively strict.
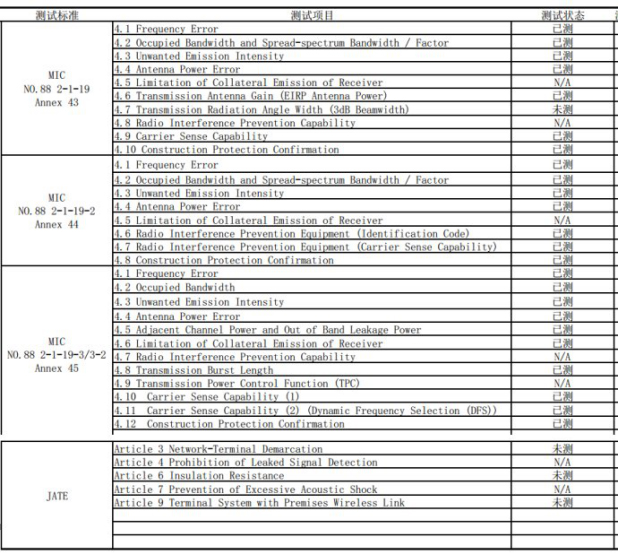
The above table shows the items for testing AP products in Japan's Technical Standard Applicability Certification and Technical Standard Applicability Recognition.
Let's take AP as an example. Assuming that this AP supports 2.4G (including support for channel 14) and also supports 5G. Then it is classified as: Class I of specific wireless devices, exemption from license (Radio Law Article 38, 2, 2, Item 1, Item 1).
The corresponding specific subcategories are:
2.4G (channels 1-13) belongs to the 5th subcategory: 2.4GHz band advanced low-power data communication system
( 2,400-2,483.5MHz (if the signal is high, the signal is high))
Certification Rules Article 2, Item 1, Item 19, Code: WWW
2.4G (channel 14) belongs to the 6th subcategory: 2.4GHz low-power data communication system
(2,471-2,497MHz (the signal is transmitted at 2,471-2,497MHz))
Certification Rules Article 2, Item 1, Item 19, No. 2, Code: GZ
5G (5.2GHz, 5.3GHz, limited to indoor use, including DFS, TPC) belongs to the 9th subcategory: 5.2 , 5.3GHz Low-power Data Communication System
Certification Rules Article 2, Paragraph 1, Item 19, No. 3, Code: XW
5G (5.6GHz, including DFS, TPC) belongs to the 10th subcategory.: 5.6GHz Low-power Data Communication System
Certification Rules Article 2, Item 1, Item 19, 3, 2, Code: YW
For certification of the Electric Communication Business Act, AP products belong to: dedicated communication line equipment and terminal equipment connected to digital data transmission equipment , code: D.
Materials required for product certification testing · Submitted materials must be in Japanese or English, and some information will be submitted to the Japanese MIC
for review
· ● Product Manual
· ● Technical Specification
· ● Block Diagram
● Schematic
● BOM
● PCB Layout
● ISO 9001 Certificate
● Antenna Specification
● Product Label
● Product Appearance Dimensions Marking Frame Diagram
● Radio Specification
● QC System Document
● Applicant Contact
Information
